AVCO Sets its Sights on Mars
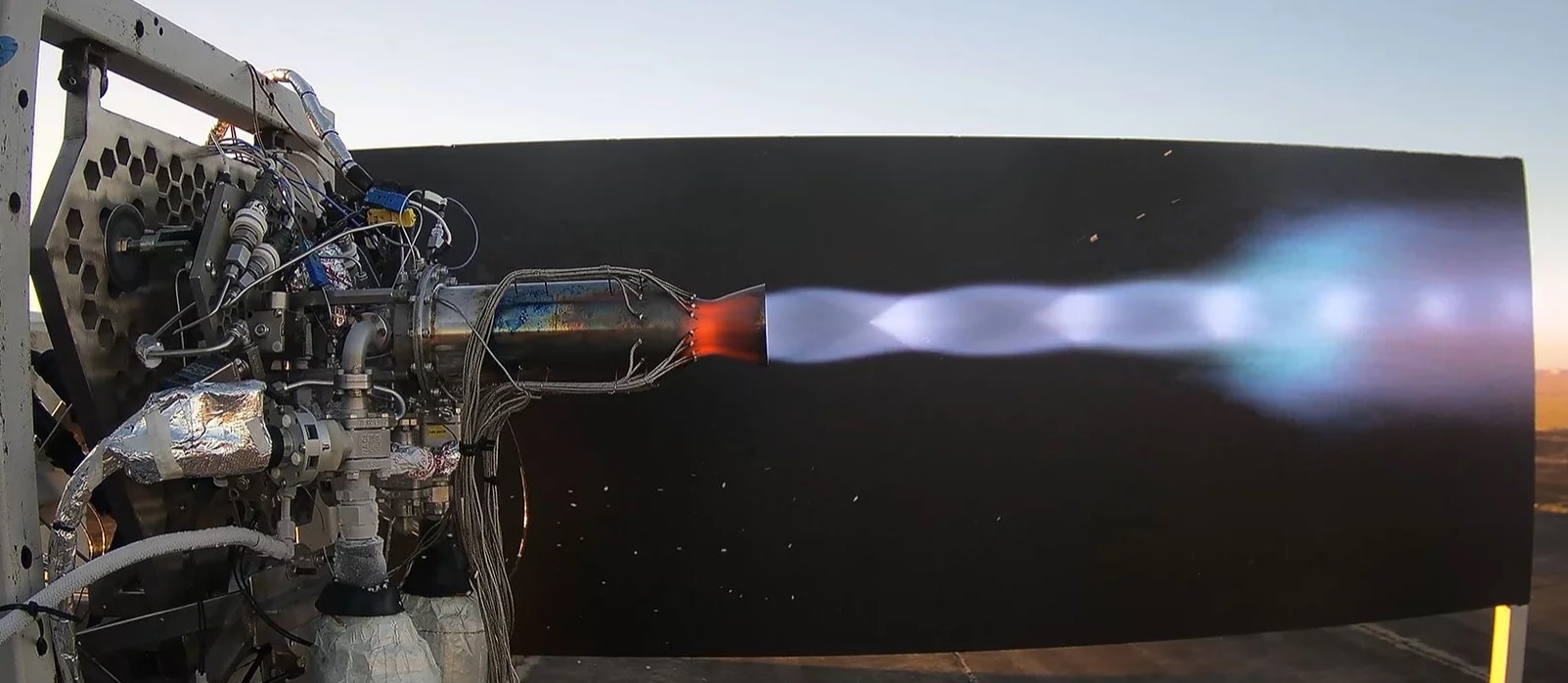 “You’re Going to The Moon” should now be quoted as “You’re Going to Mars.” From the 1990s downturn in the aerospace industry to today’s exponential growth, the demand for precision flow control and flow measurement has continued to follow the same growth trajectory. The focus of Alloy Valves and Control (AVCO) has been on the need to fulfill the requirements of research and development for rocket engine design, test stands, rocket propellant and life support systems for space travel in both unmanned and manned space vehicles.
“You’re Going to The Moon” should now be quoted as “You’re Going to Mars.” From the 1990s downturn in the aerospace industry to today’s exponential growth, the demand for precision flow control and flow measurement has continued to follow the same growth trajectory. The focus of Alloy Valves and Control (AVCO) has been on the need to fulfill the requirements of research and development for rocket engine design, test stands, rocket propellant and life support systems for space travel in both unmanned and manned space vehicles.


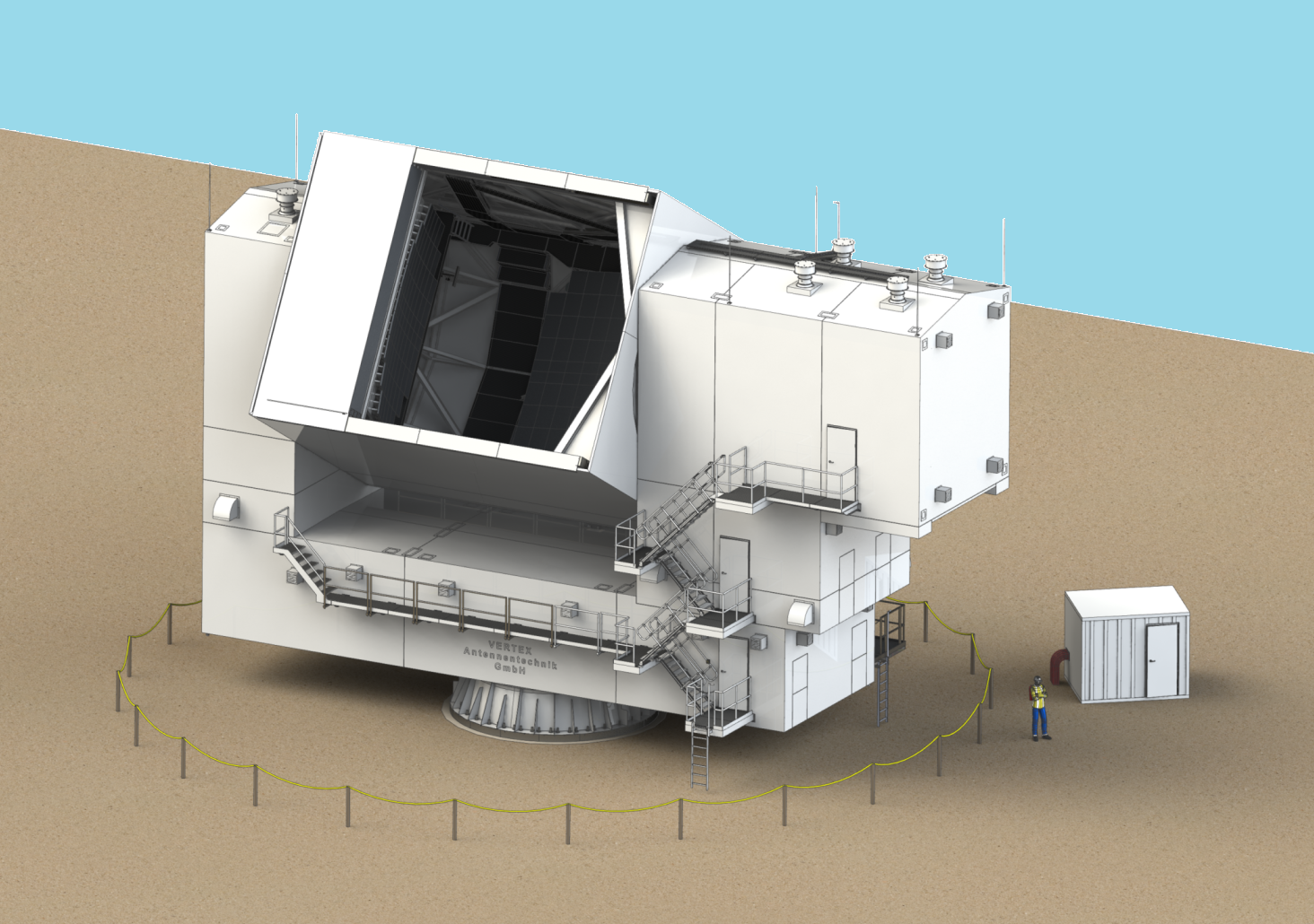 For the past six years, CCAT Observatory Inc., a nonprofit research organization formed by more than a dozen academic institutions led by Cornell University, has been developing a new telescope, the Fred Young Submillimeter Telescope (FYST, pronounced “feast”) and its supporting infrastructure to observe at submillimeter wavelengths. The infrastructure is currently under construction at an altitude of 5,600 m near the summit of Cerro Chajnantor in the Atacama Desert of northern Chile, one of the driest places on Earth. Since water vapor absorbs the wavelengths of interest, the site is arguably the best ground-based location for submillimeter observations due to its thin, ultradry atmosphere. Once complete, it will be the second highest observatory in the world.
For the past six years, CCAT Observatory Inc., a nonprofit research organization formed by more than a dozen academic institutions led by Cornell University, has been developing a new telescope, the Fred Young Submillimeter Telescope (FYST, pronounced “feast”) and its supporting infrastructure to observe at submillimeter wavelengths. The infrastructure is currently under construction at an altitude of 5,600 m near the summit of Cerro Chajnantor in the Atacama Desert of northern Chile, one of the driest places on Earth. Since water vapor absorbs the wavelengths of interest, the site is arguably the best ground-based location for submillimeter observations due to its thin, ultradry atmosphere. Once complete, it will be the second highest observatory in the world.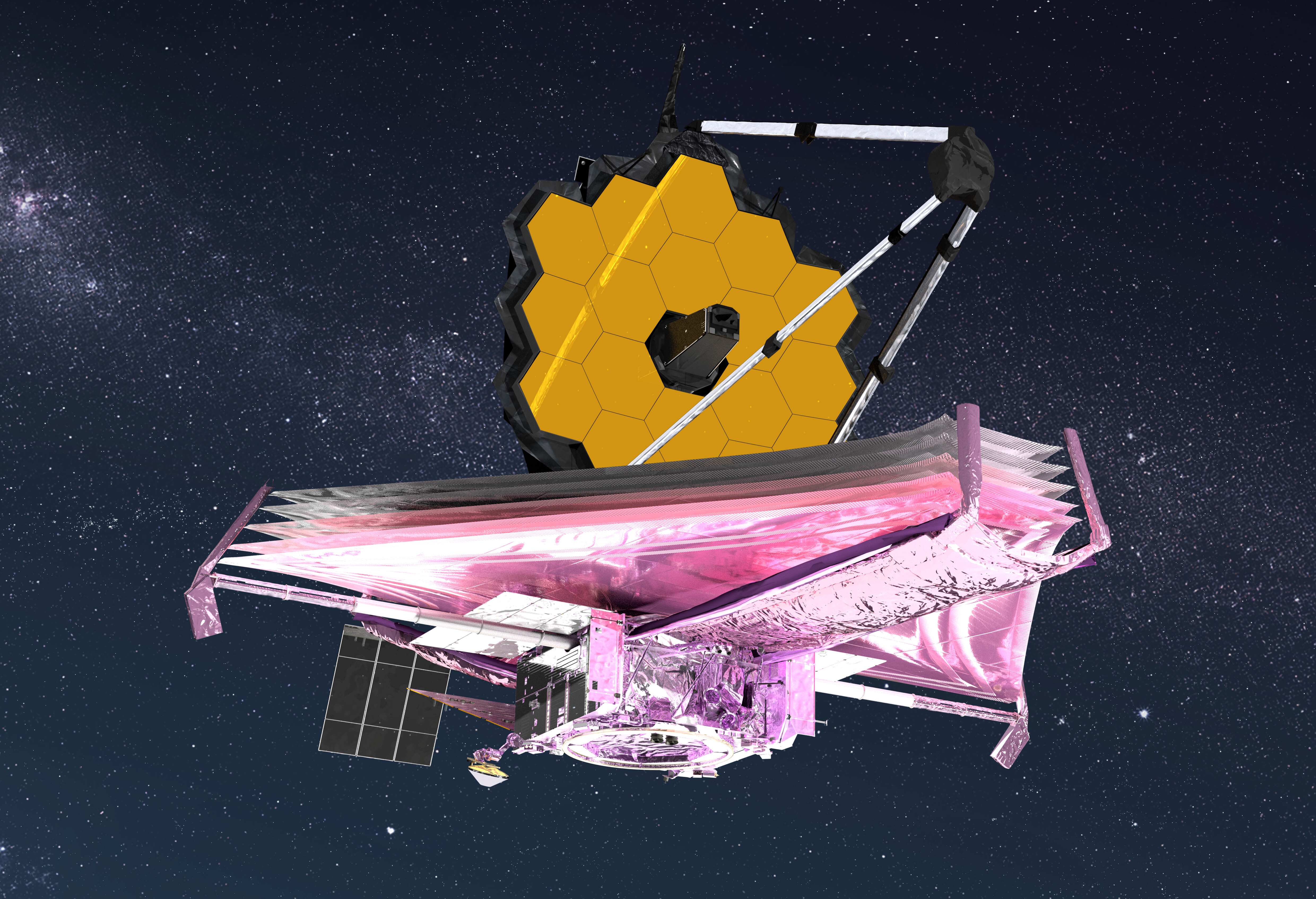  James Webb Space Telescope-“I’m Back in the Saddle Again!” – It’s likely anyone reading this article has heard about the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST). The telescope launched on December 25, 2021 (EST) with much fanfare. Over the next month, it traveled to its observation location at the L2 Lagrange point in the earth-sun gravitational system. It has been sitting comfortably at this saddle point for well over a year. Cooling of the instrument didn’t wait until reaching this point. Oh no, this began shortly after the launch from the spaceport in French Guiana because the majority of the telescope was cooled passively via thermal radiation to outer space.
James Webb Space Telescope-“I’m Back in the Saddle Again!” – It’s likely anyone reading this article has heard about the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST). The telescope launched on December 25, 2021 (EST) with much fanfare. Over the next month, it traveled to its observation location at the L2 Lagrange point in the earth-sun gravitational system. It has been sitting comfortably at this saddle point for well over a year. Cooling of the instrument didn’t wait until reaching this point. Oh no, this began shortly after the launch from the spaceport in French Guiana because the majority of the telescope was cooled passively via thermal radiation to outer space.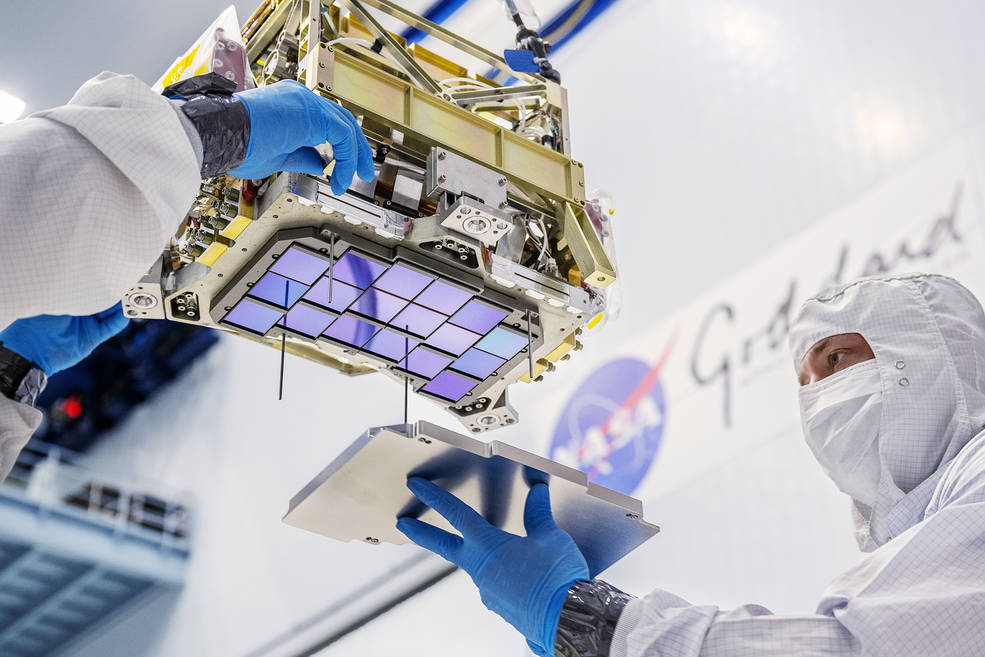  The heart of NASA’s Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope was recently delivered to Ball Aerospace in Boulder, Colo., for integration into the Wide Field Instrument (WFI). Called the Focal Plane System (FPS), it serves as the core of Roman’s camera. When the mission launches by May 2027, astronomers will use this system to gather exquisite images to help unravel the secrets of dark energy and dark matter, discover exoplanets and explore many topics in infrared astrophysics.
The heart of NASA’s Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope was recently delivered to Ball Aerospace in Boulder, Colo., for integration into the Wide Field Instrument (WFI). Called the Focal Plane System (FPS), it serves as the core of Roman’s camera. When the mission launches by May 2027, astronomers will use this system to gather exquisite images to help unravel the secrets of dark energy and dark matter, discover exoplanets and explore many topics in infrared astrophysics.  XMA, with its space heritage spanning from low-Earth orbit (LEO) to deep space exploration units, embarked on a journey to enter the supply chain for quantum computing more than 10 years ago. The driving force behind this industry expansion was XMA’s success in cryogenic temperatures down to approximately 4 K in space environments. XMA managed to strike the perfect balance between rugged materials that remained non-superconductive at cold temperatures and low-mass products. When quantum technologists cooled these components to millikelvin temperatures, the specifications remained unchanged. This consistent performance from ambient to cryogenic conditions has become XMA’s baseline for success. With the cross-pollination of knowledge between the space and quantum industries, XMA has experienced steady growth in both sectors, thanks to its novel designs and successful environmental testing. As space exploration and quantum computing continue to advance, XMA leverages the newfound knowledge from each industry to improve the other.
XMA, with its space heritage spanning from low-Earth orbit (LEO) to deep space exploration units, embarked on a journey to enter the supply chain for quantum computing more than 10 years ago. The driving force behind this industry expansion was XMA’s success in cryogenic temperatures down to approximately 4 K in space environments. XMA managed to strike the perfect balance between rugged materials that remained non-superconductive at cold temperatures and low-mass products. When quantum technologists cooled these components to millikelvin temperatures, the specifications remained unchanged. This consistent performance from ambient to cryogenic conditions has become XMA’s baseline for success. With the cross-pollination of knowledge between the space and quantum industries, XMA has experienced steady growth in both sectors, thanks to its novel designs and successful environmental testing. As space exploration and quantum computing continue to advance, XMA leverages the newfound knowledge from each industry to improve the other.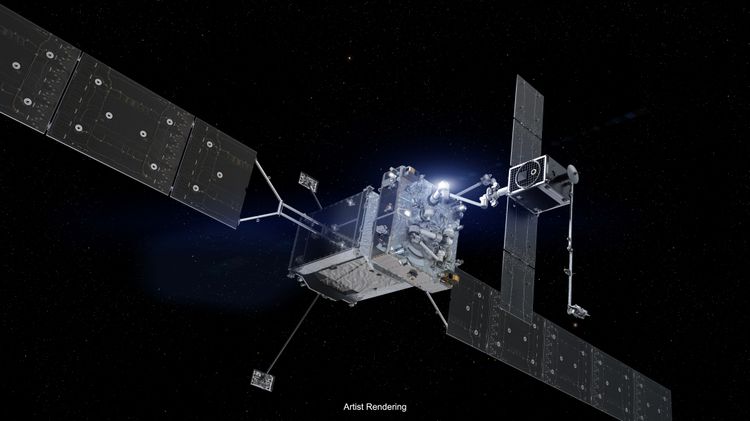 Northrop Grumman Corporation’s
Northrop Grumman Corporation’s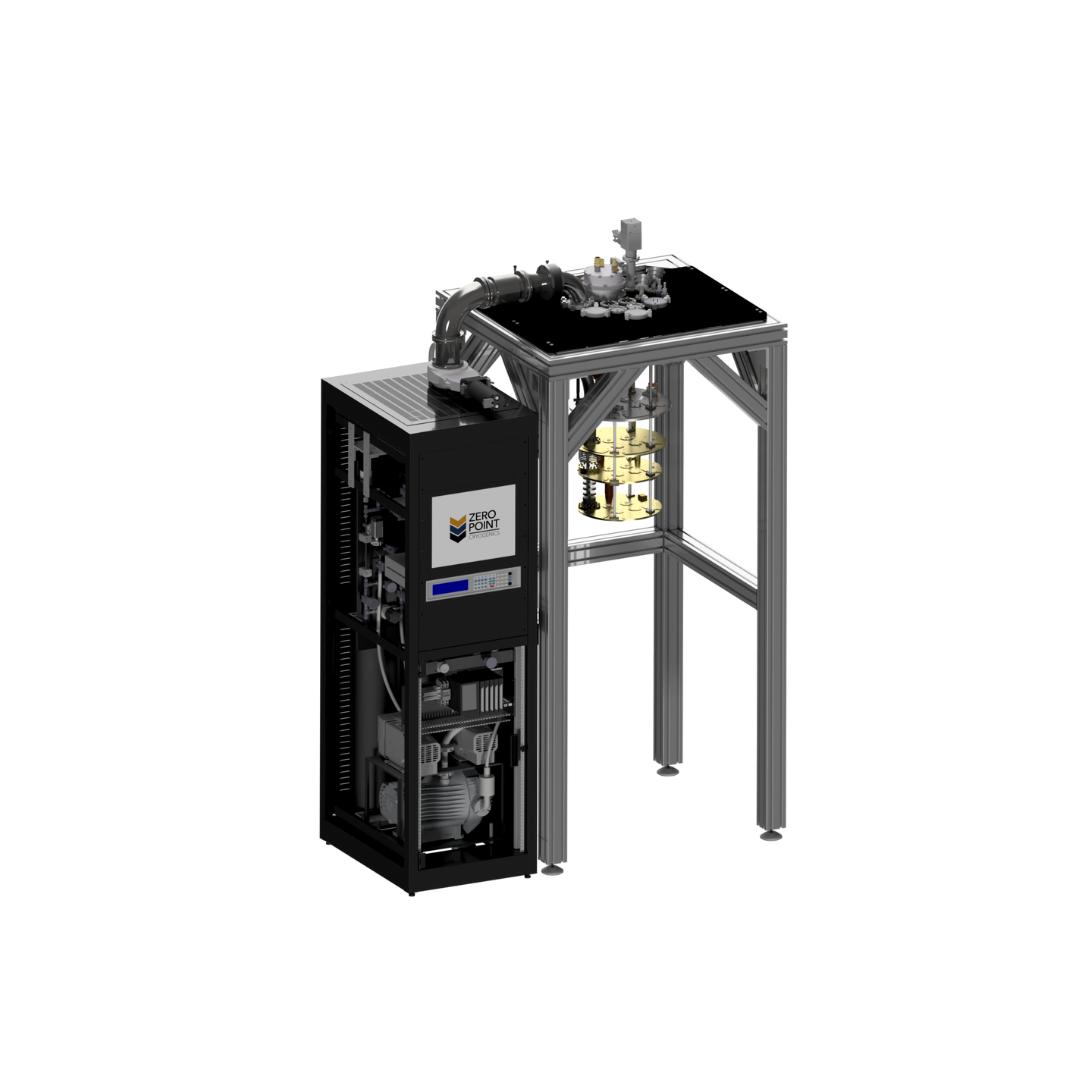  Understanding the basic principles of dilution refrigeration is essential for operating a ZPC dilution refrigerator effectively. While there are comprehensive guides available on the subject, we provide a condensed overview for quick reference.
Understanding the basic principles of dilution refrigeration is essential for operating a ZPC dilution refrigerator effectively. While there are comprehensive guides available on the subject, we provide a condensed overview for quick reference.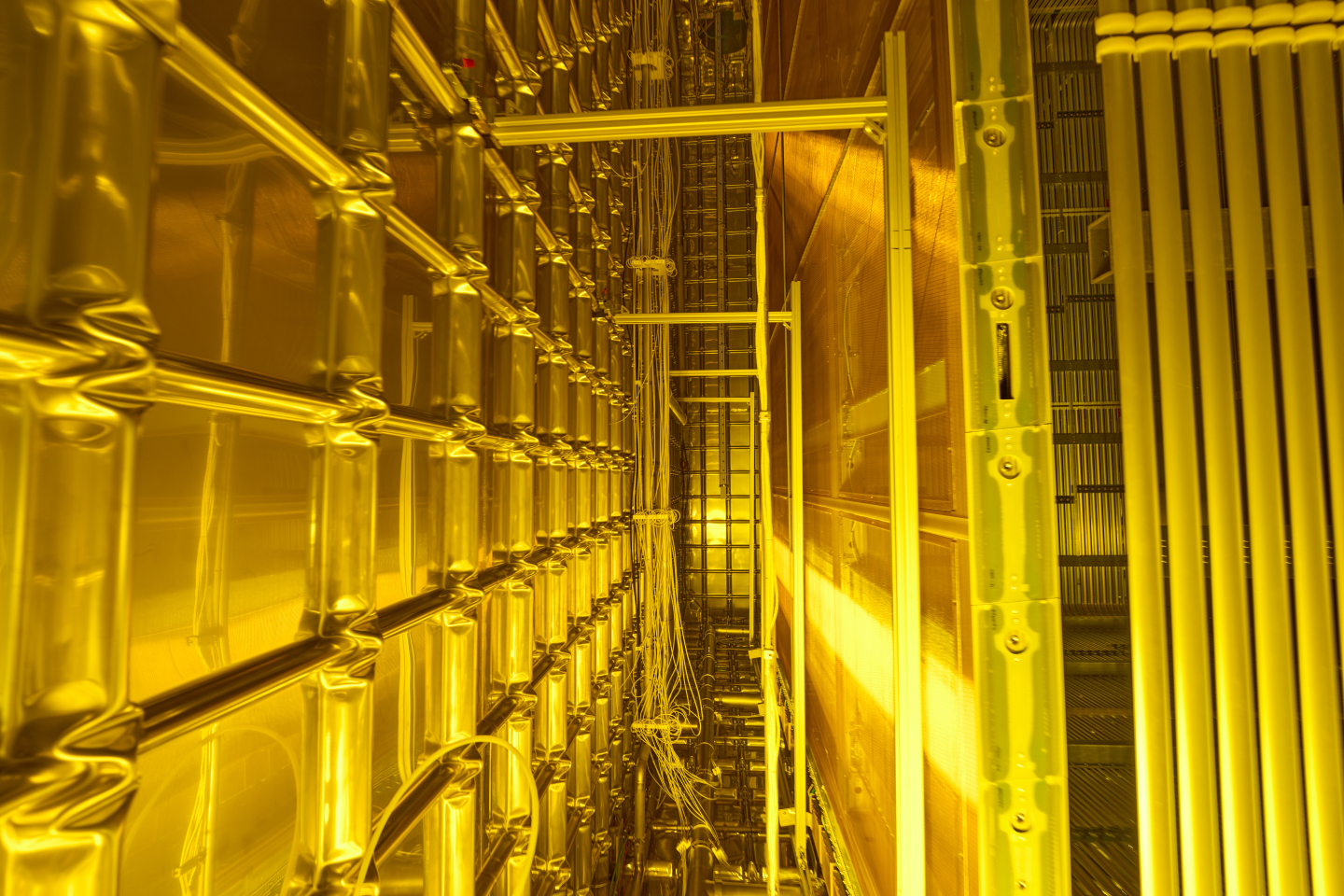  At CERN’s Neutrino Platform on the Laboratory’s Prévessin site in France sit two large boxes encased in a red grating. Inside these boxes are vast chambers surrounded by shiny stainless steel. The boxes are the cryostat modules of the ProtoDUNE experiment. Despite their large size, they are tiny in comparison to the future size of their successors for the Deep Underground Neutrino Experiment (DUNE), a vast neutrino experiment currently being built in the USA. The Neutrino Platform also houses an assembly station for the Tokai to Kamioka (T2K) experiment, another vast neutrino facility in Japan.
At CERN’s Neutrino Platform on the Laboratory’s Prévessin site in France sit two large boxes encased in a red grating. Inside these boxes are vast chambers surrounded by shiny stainless steel. The boxes are the cryostat modules of the ProtoDUNE experiment. Despite their large size, they are tiny in comparison to the future size of their successors for the Deep Underground Neutrino Experiment (DUNE), a vast neutrino experiment currently being built in the USA. The Neutrino Platform also houses an assembly station for the Tokai to Kamioka (T2K) experiment, another vast neutrino facility in Japan. Swift Aircraft, the visionary company behind the innovative British aerobatic light aircraft called the Swift, has joined forces with a team of British innovators to drive sustainable flight forward. Their collaboration is supported by the Project MONET contract, awarded by the UK Ministry of Defence (MoD), aimed at demonstrating technologies for achieving net-zero emissions during flight.
Swift Aircraft, the visionary company behind the innovative British aerobatic light aircraft called the Swift, has joined forces with a team of British innovators to drive sustainable flight forward. Their collaboration is supported by the Project MONET contract, awarded by the UK Ministry of Defence (MoD), aimed at demonstrating technologies for achieving net-zero emissions during flight.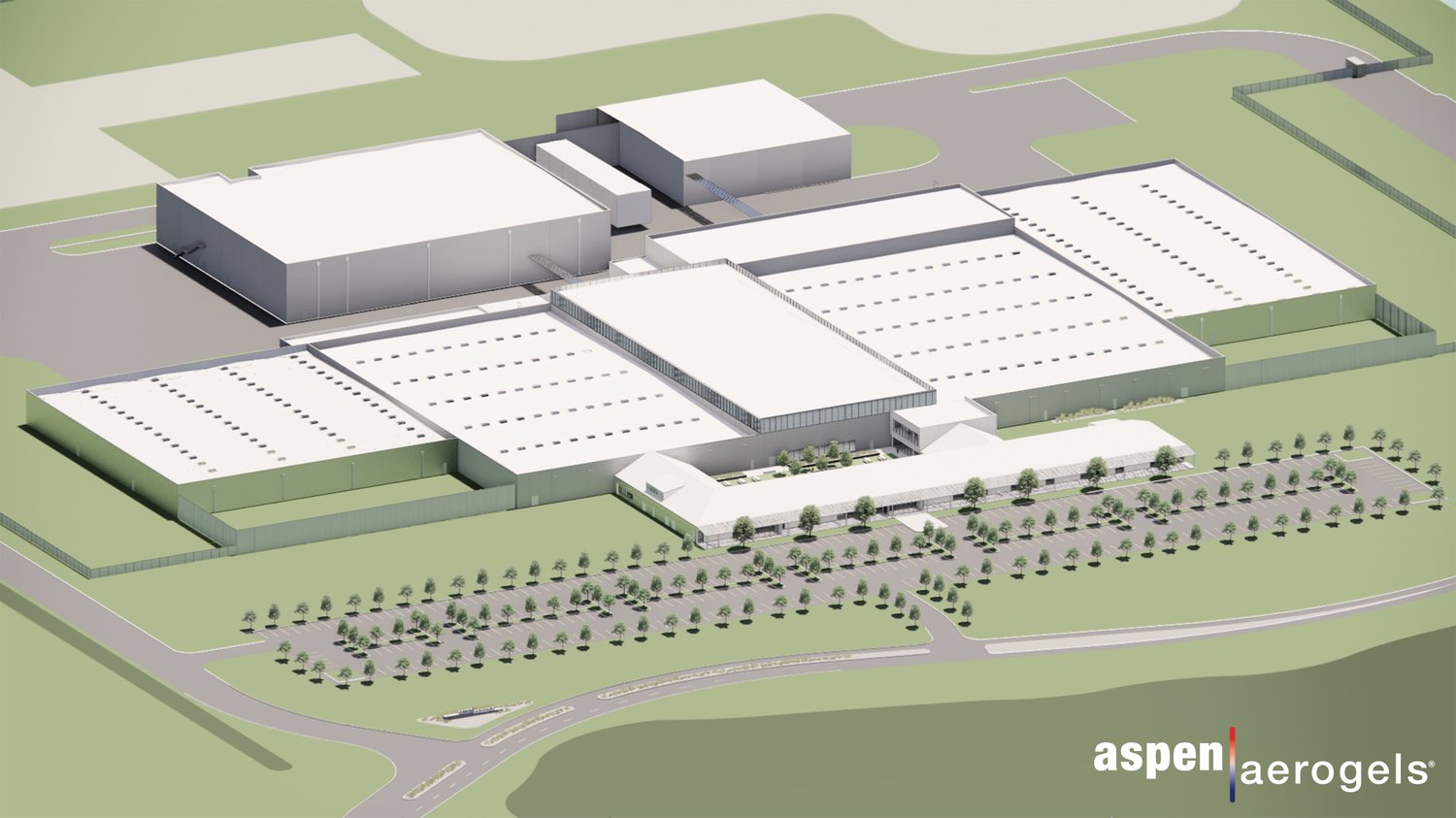 Aspen Aerogels, a leading technology company specializing in aerogel-based sustainability and electrification solutions, has announced the grand opening of its state-of-the-art engineering and rapid prototyping facility in Marlborough, MA. This 59,000-square-foot facility, known as the Advanced Thermal Barrier Center (ATBC), will serve as the engineering hub for PyroThin cell-to-cell barriers, which play a vital role in optimizing the safety and performance of battery packs for the rapidly growing eMobility and energy storage system (ESS) markets.
Aspen Aerogels, a leading technology company specializing in aerogel-based sustainability and electrification solutions, has announced the grand opening of its state-of-the-art engineering and rapid prototyping facility in Marlborough, MA. This 59,000-square-foot facility, known as the Advanced Thermal Barrier Center (ATBC), will serve as the engineering hub for PyroThin cell-to-cell barriers, which play a vital role in optimizing the safety and performance of battery packs for the rapidly growing eMobility and energy storage system (ESS) markets. ![Image: Experiments on a family of cuprate superconductors resolve discrepancies in previous work and elucidate why the critical temperature varies with pressure. Credit: A. C. Mark et al. [1] Image: Experiments on a family of cuprate superconductors resolve discrepancies in previous work and elucidate why the critical temperature varies with pressure. Credit: A. C. Mark et al. [1]](https://cryo.memberclicks.net/assets/news/Squeezing%20superconductors.png) How electrons pair in cuprate superconductors depends, in part, on the crystalline landscape the electrons occupy. That landscape can be altered by applying pressure, which in turn causes the critical temperature (Tc) in some cuprates to rise, fall, and rise again as the pressure grows. But are the changes in Tc due to the atoms being pressed into a new crystalline structure or just being squeezed closer together? Experimental evidence is contradictory. To resolve the question, Alexander Mark of the University of Illinois Chicago and his collaborators performed experiments on the three members of the BSCCO family of cuprates [
How electrons pair in cuprate superconductors depends, in part, on the crystalline landscape the electrons occupy. That landscape can be altered by applying pressure, which in turn causes the critical temperature (Tc) in some cuprates to rise, fall, and rise again as the pressure grows. But are the changes in Tc due to the atoms being pressed into a new crystalline structure or just being squeezed closer together? Experimental evidence is contradictory. To resolve the question, Alexander Mark of the University of Illinois Chicago and his collaborators performed experiments on the three members of the BSCCO family of cuprates [ On Tuesday, May 22, NASA’s
On Tuesday, May 22, NASA’s 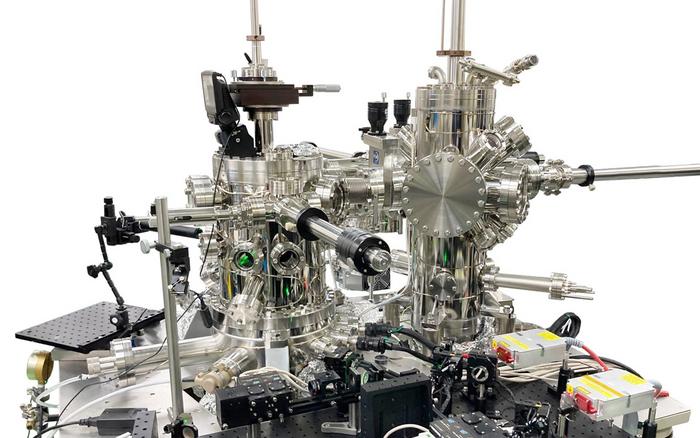 Semiconductors are foundational components of modern energy, communication, and myriad other technologies. Research on tailoring the underlying nanostructure of semiconductors for optimizing device performance has been ongoing for decades. Now, in a study recently published in Scientific Reports, researchers from the University of Tsukuba and collaborating partner UNISOKU Co., LTD., have facilitated technology development—easy-to-use, time-resolved scanning tunneling microscopy (STM)—for measuring the movement of electrons in nanostructures at high temporal and spatial resolution, in a manner that will be invaluable for optimizing nanostructure performance.
Semiconductors are foundational components of modern energy, communication, and myriad other technologies. Research on tailoring the underlying nanostructure of semiconductors for optimizing device performance has been ongoing for decades. Now, in a study recently published in Scientific Reports, researchers from the University of Tsukuba and collaborating partner UNISOKU Co., LTD., have facilitated technology development—easy-to-use, time-resolved scanning tunneling microscopy (STM)—for measuring the movement of electrons in nanostructures at high temporal and spatial resolution, in a manner that will be invaluable for optimizing nanostructure performance.
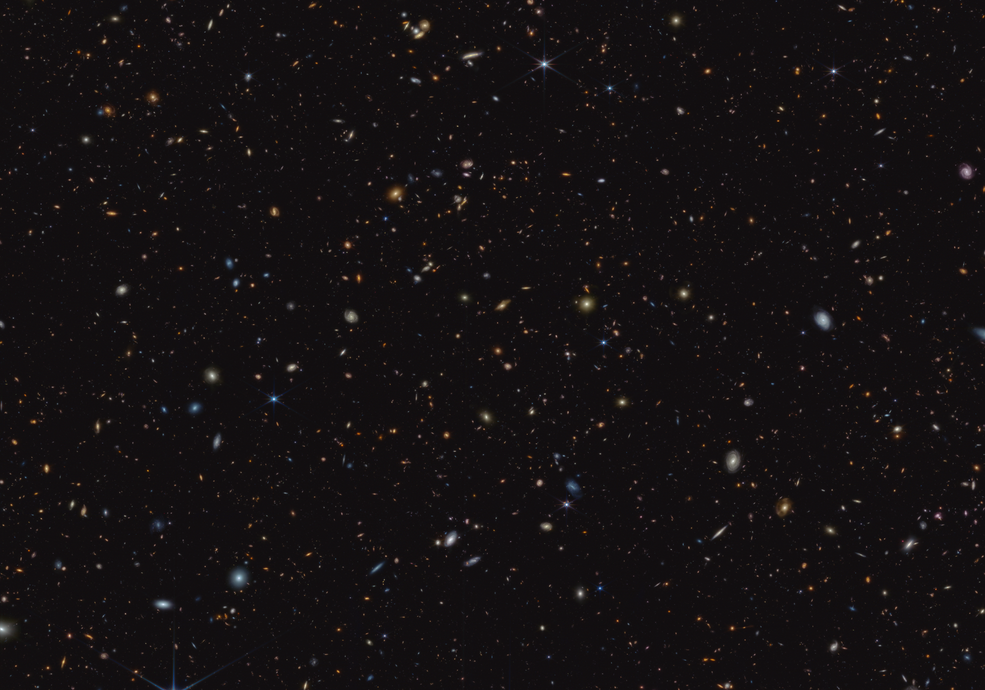 Among the most fundamental questions in astronomy: how did the first stars and galaxies form? NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope is already providing new insights into this question. One of the largest programs in Webb’s first year of science is the JWST Advanced Deep Extragalactic Survey, or JADES, which will devote about 32 days of telescope time to uncover and characterize faint, distant galaxies. While the data is still coming in, JADES already has discovered hundreds of galaxies that existed when the universe was less than 600 million years old. The team also has identified galaxies sparkling with a multitude of young, hot stars.
Among the most fundamental questions in astronomy: how did the first stars and galaxies form? NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope is already providing new insights into this question. One of the largest programs in Webb’s first year of science is the JWST Advanced Deep Extragalactic Survey, or JADES, which will devote about 32 days of telescope time to uncover and characterize faint, distant galaxies. While the data is still coming in, JADES already has discovered hundreds of galaxies that existed when the universe was less than 600 million years old. The team also has identified galaxies sparkling with a multitude of young, hot stars.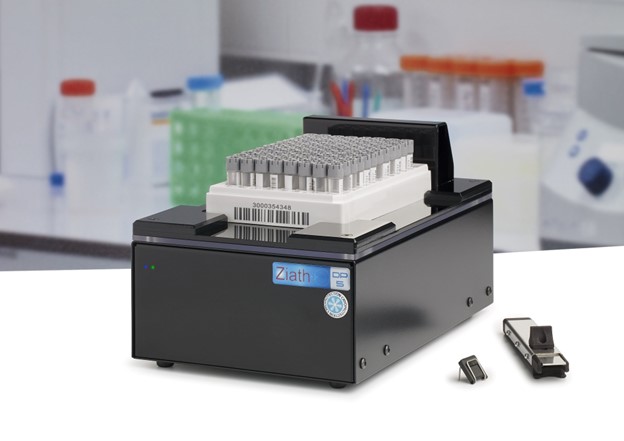 Ziath, an Azenta Life Sciences company, announced a revolution in cryogenic sample management – the Ri-Track Mirage 2D barcoded tube whole rack reader.
Ziath, an Azenta Life Sciences company, announced a revolution in cryogenic sample management – the Ri-Track Mirage 2D barcoded tube whole rack reader.  Precision measurements reveal connection between electron density and atomic arrangements in charge-ordered states of a superconducting copper-oxide material. Researchers at the Brookhaven National Laboratory have discovered a direct connection between the disappearance of certain atomic vibrations and the emergence of a “charge density wave” in superconducting copper-oxide materials. This discovery, achieved through precision measurement, uncovers a vital relationship between atomic structure and charge distribution, advancing our understanding of superconductivity.
Precision measurements reveal connection between electron density and atomic arrangements in charge-ordered states of a superconducting copper-oxide material. Researchers at the Brookhaven National Laboratory have discovered a direct connection between the disappearance of certain atomic vibrations and the emergence of a “charge density wave” in superconducting copper-oxide materials. This discovery, achieved through precision measurement, uncovers a vital relationship between atomic structure and charge distribution, advancing our understanding of superconductivity. The stable isotopes hydrogen and oxygen (δ2H and δ18O, respectively) in soil water are widely used in ecological studies, which rely on the accurate extraction of unfractionated water from different soil types. Cryogenic vacuum distillation (CVD) is the laboratory-based technique most widely used in eco-hydrological studies. However, the reliability of this technique in reflecting soil water δ2H and δ18O is still of concern.
The stable isotopes hydrogen and oxygen (δ2H and δ18O, respectively) in soil water are widely used in ecological studies, which rely on the accurate extraction of unfractionated water from different soil types. Cryogenic vacuum distillation (CVD) is the laboratory-based technique most widely used in eco-hydrological studies. However, the reliability of this technique in reflecting soil water δ2H and δ18O is still of concern. The pressure to reduce greenhouse gas emissions continues as does the search for ‘greener energy solutions’ and one of the consequences of this is significant growth in the use of Liquid Natural Gas for marine applications. LNG has long been regarded as a sustainable fuel and has gained significant traction as a viable alternative for a wide range of commercial transport applications, including marine and shipping. It is estimated that 3% of global greenhouse gas emissions such as carbon dioxide is generated by maritime traffic, which is why the International Maritime Organization (IMO) is increasingly looking to reduce CO2 emissions. While LNG is a much ‘greener’ fuel than the highly viscous diesel fuels typically used to power container ships and cruise liners, it does present significant challenges to fuel systems and pumps, specifically dealing with extreme (cryogenic) temperatures.
The pressure to reduce greenhouse gas emissions continues as does the search for ‘greener energy solutions’ and one of the consequences of this is significant growth in the use of Liquid Natural Gas for marine applications. LNG has long been regarded as a sustainable fuel and has gained significant traction as a viable alternative for a wide range of commercial transport applications, including marine and shipping. It is estimated that 3% of global greenhouse gas emissions such as carbon dioxide is generated by maritime traffic, which is why the International Maritime Organization (IMO) is increasingly looking to reduce CO2 emissions. While LNG is a much ‘greener’ fuel than the highly viscous diesel fuels typically used to power container ships and cruise liners, it does present significant challenges to fuel systems and pumps, specifically dealing with extreme (cryogenic) temperatures.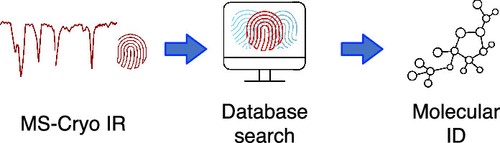 Researchers from Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne in Switzerland have developed a new approach for identifying isomeric and isobaric metabolites using high-resolution ion mobility spectrometry (IMS) and cryogenic infrared (IR) spectroscopy. The complex structure of metabolites has made their identification challenging, and analytical standards are often required to confirm their presence in a sample. However, the new approach can separate isomeric metabolites in a matter of milliseconds and provide highly structured IR fingerprints for their unambiguous identification. Additionally, this approach allows for the automatic identification of metabolite isomers by comparing their IR fingerprints with those in a database, thereby eliminating the need for analytical standards.
Researchers from Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne in Switzerland have developed a new approach for identifying isomeric and isobaric metabolites using high-resolution ion mobility spectrometry (IMS) and cryogenic infrared (IR) spectroscopy. The complex structure of metabolites has made their identification challenging, and analytical standards are often required to confirm their presence in a sample. However, the new approach can separate isomeric metabolites in a matter of milliseconds and provide highly structured IR fingerprints for their unambiguous identification. Additionally, this approach allows for the automatic identification of metabolite isomers by comparing their IR fingerprints with those in a database, thereby eliminating the need for analytical standards. High-performance, highly reliable, long-lasting storage tanks for transporting hydrogen& helium molecules around the globe.
High-performance, highly reliable, long-lasting storage tanks for transporting hydrogen& helium molecules around the globe.