Novel Cryogenic Nanopositioning Technique Progresses into the Quantum Sensing Decade
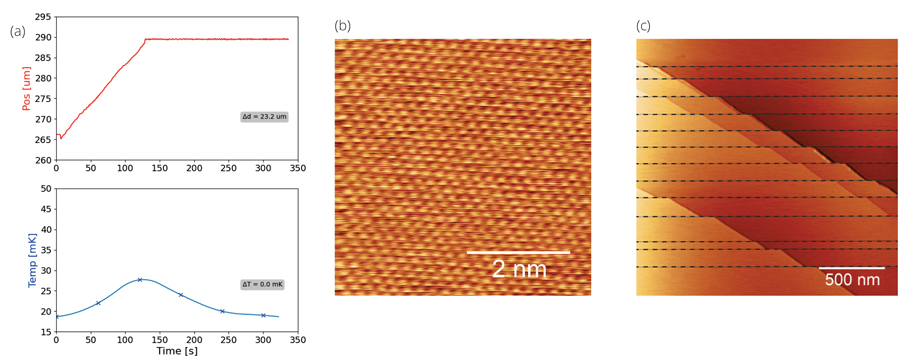 Quantum Sensing: Necessity for low temperature and low vibrations-Most quantum states are only visible and controllable when the thermal energy KBT is comparable or smaller than the energy difference ΔE between the quantum states. Therefore, to see the quantum properties of materials or devices, they often need to be cooled to and maintained at millikelvin temperatures. In the last ten years, we have seen great progress in improving the accessibility to millikelvin environments via advanced cryogenic platforms offered by industry. On the basis of these platforms, the application can be developed that would allow probing quantum states of materials or devices, for example by means of Scanning Probe Microscopy (SPM) techniques. However, for low temperature SPM techniques, besides the low temperature, low vibrations are also essential. First, the interaction distance between probe and quantum state needs to be maintained and second, in case of force-sensors like M(R)FM, the sensor needs to be decoupled from force-noise due to accelerations. It is to this end that quantum sensing will require progression towards low temperature and low vibration environments to use quantum-enhanced probe sensors for opening a new paradigm of Scanning Probe Microscopy: qSPM.
Quantum Sensing: Necessity for low temperature and low vibrations-Most quantum states are only visible and controllable when the thermal energy KBT is comparable or smaller than the energy difference ΔE between the quantum states. Therefore, to see the quantum properties of materials or devices, they often need to be cooled to and maintained at millikelvin temperatures. In the last ten years, we have seen great progress in improving the accessibility to millikelvin environments via advanced cryogenic platforms offered by industry. On the basis of these platforms, the application can be developed that would allow probing quantum states of materials or devices, for example by means of Scanning Probe Microscopy (SPM) techniques. However, for low temperature SPM techniques, besides the low temperature, low vibrations are also essential. First, the interaction distance between probe and quantum state needs to be maintained and second, in case of force-sensors like M(R)FM, the sensor needs to be decoupled from force-noise due to accelerations. It is to this end that quantum sensing will require progression towards low temperature and low vibration environments to use quantum-enhanced probe sensors for opening a new paradigm of Scanning Probe Microscopy: qSPM.
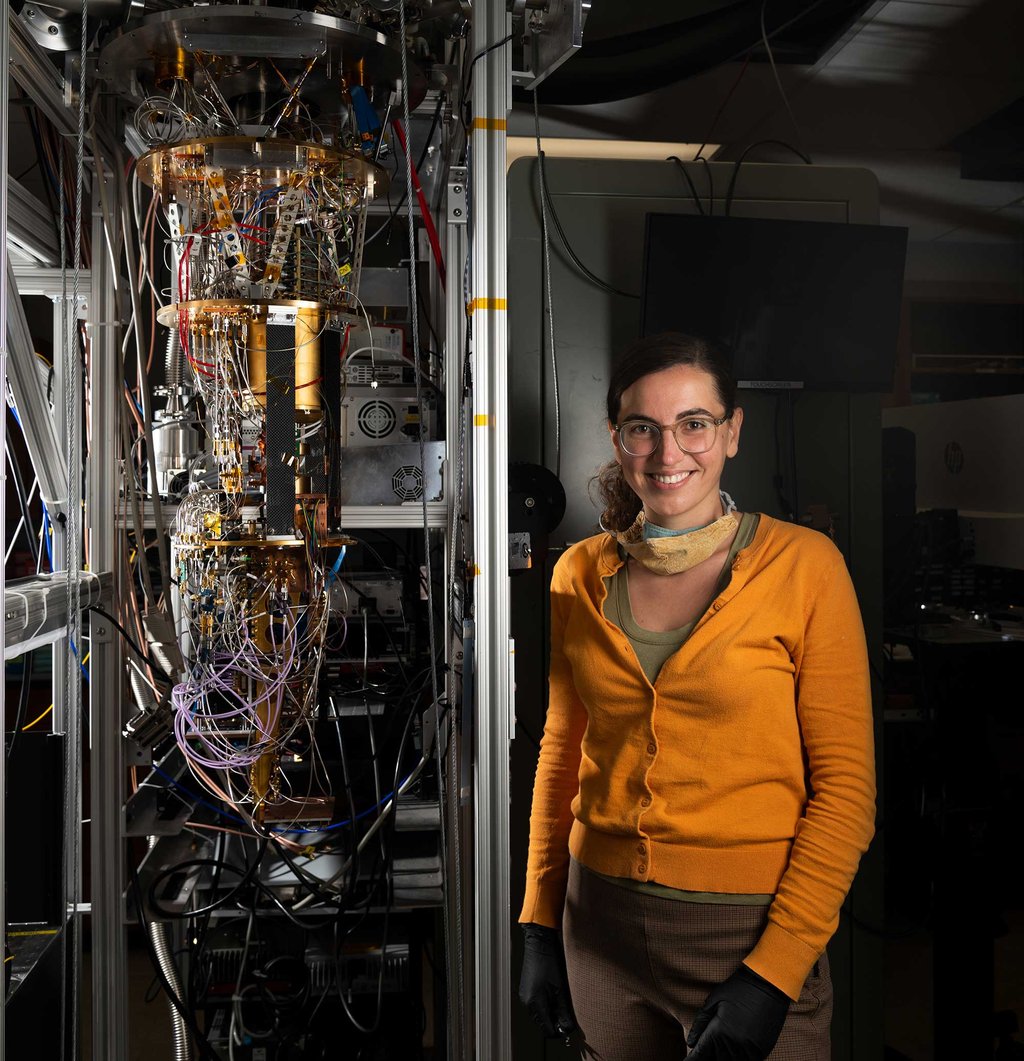

 A new JPL- and Caltech-developed detector could transform how quantum computers located thousands of miles apart exchange huge quantities of quantum data. Quantum computers hold the promise of operating millions of times faster than conventional computers. But to communicate over long distances, quantum computers will need a dedicated quantum communications network.
A new JPL- and Caltech-developed detector could transform how quantum computers located thousands of miles apart exchange huge quantities of quantum data. Quantum computers hold the promise of operating millions of times faster than conventional computers. But to communicate over long distances, quantum computers will need a dedicated quantum communications network.
 Energy Sector and Metallic Materials
Energy Sector and Metallic Materials The Second Target Station (STS) is the future of forefront neutron scattering science at Oak Ridge National Laboratory, which started with the first neutron scattering measurements in the 1940s at the X-10 Graphite Reactor and continues today at the High Flux Isotope Reactor (HFIR) and Spallation Neutron Source (SNS). STS will be a 700 kW, 15 Hz pulsed-spallation neutron source designed to provide the world’s highest peak of brightness cold neutron beams, meeting the demand for neutron scattering resources for physical, chemical, biological, geological, materials and human health sciences. The STS will utilize one out of every four proton pulses from the SNS accelerator, delivering the 1µs pulses to a rotating water-cooled tungsten target and producing neutrons by the spallation process. To convert high energy spallation neutrons to high brightness cold neutron beams, two compact liquid hydrogen moderators are located adjacent to the target’s peak neutron production zone and surrounded by light water premoderators and beryllium reflectors to increase neutron flux.
The Second Target Station (STS) is the future of forefront neutron scattering science at Oak Ridge National Laboratory, which started with the first neutron scattering measurements in the 1940s at the X-10 Graphite Reactor and continues today at the High Flux Isotope Reactor (HFIR) and Spallation Neutron Source (SNS). STS will be a 700 kW, 15 Hz pulsed-spallation neutron source designed to provide the world’s highest peak of brightness cold neutron beams, meeting the demand for neutron scattering resources for physical, chemical, biological, geological, materials and human health sciences. The STS will utilize one out of every four proton pulses from the SNS accelerator, delivering the 1µs pulses to a rotating water-cooled tungsten target and producing neutrons by the spallation process. To convert high energy spallation neutrons to high brightness cold neutron beams, two compact liquid hydrogen moderators are located adjacent to the target’s peak neutron production zone and surrounded by light water premoderators and beryllium reflectors to increase neutron flux.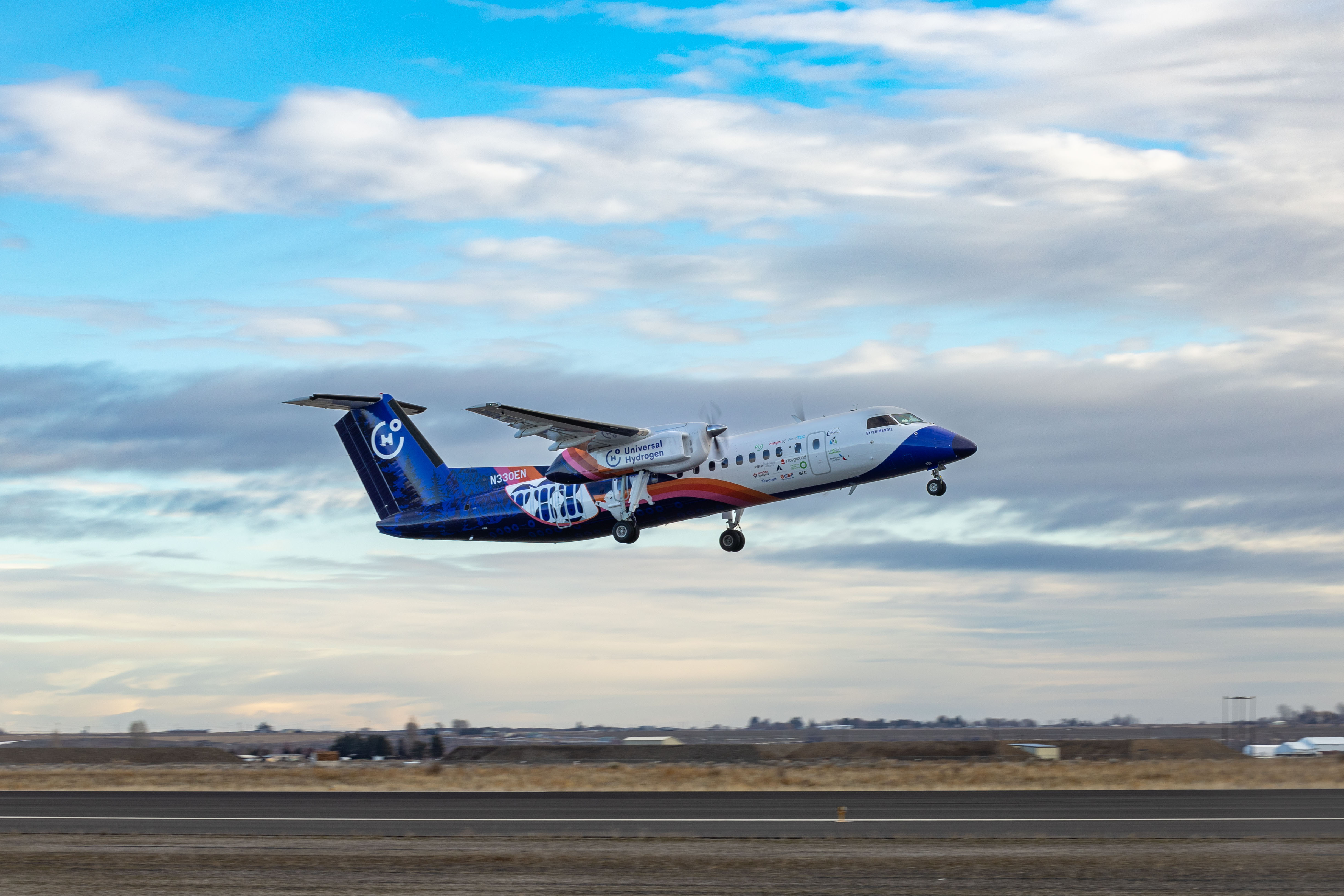  Hydrogen has been touted as the fuel of the future, but challenges remain in improving the storage efficiency of liquefied hydrogen fuel for large scale commercial transport and storage. Researchers from South Korea have conducted experiments and simulations to investigate the heat flows and phase changes within a cryogenic fuel tank using multiphase thermal flow simulations, with the goal of designing safe and efficient cryotanks.
Hydrogen has been touted as the fuel of the future, but challenges remain in improving the storage efficiency of liquefied hydrogen fuel for large scale commercial transport and storage. Researchers from South Korea have conducted experiments and simulations to investigate the heat flows and phase changes within a cryogenic fuel tank using multiphase thermal flow simulations, with the goal of designing safe and efficient cryotanks.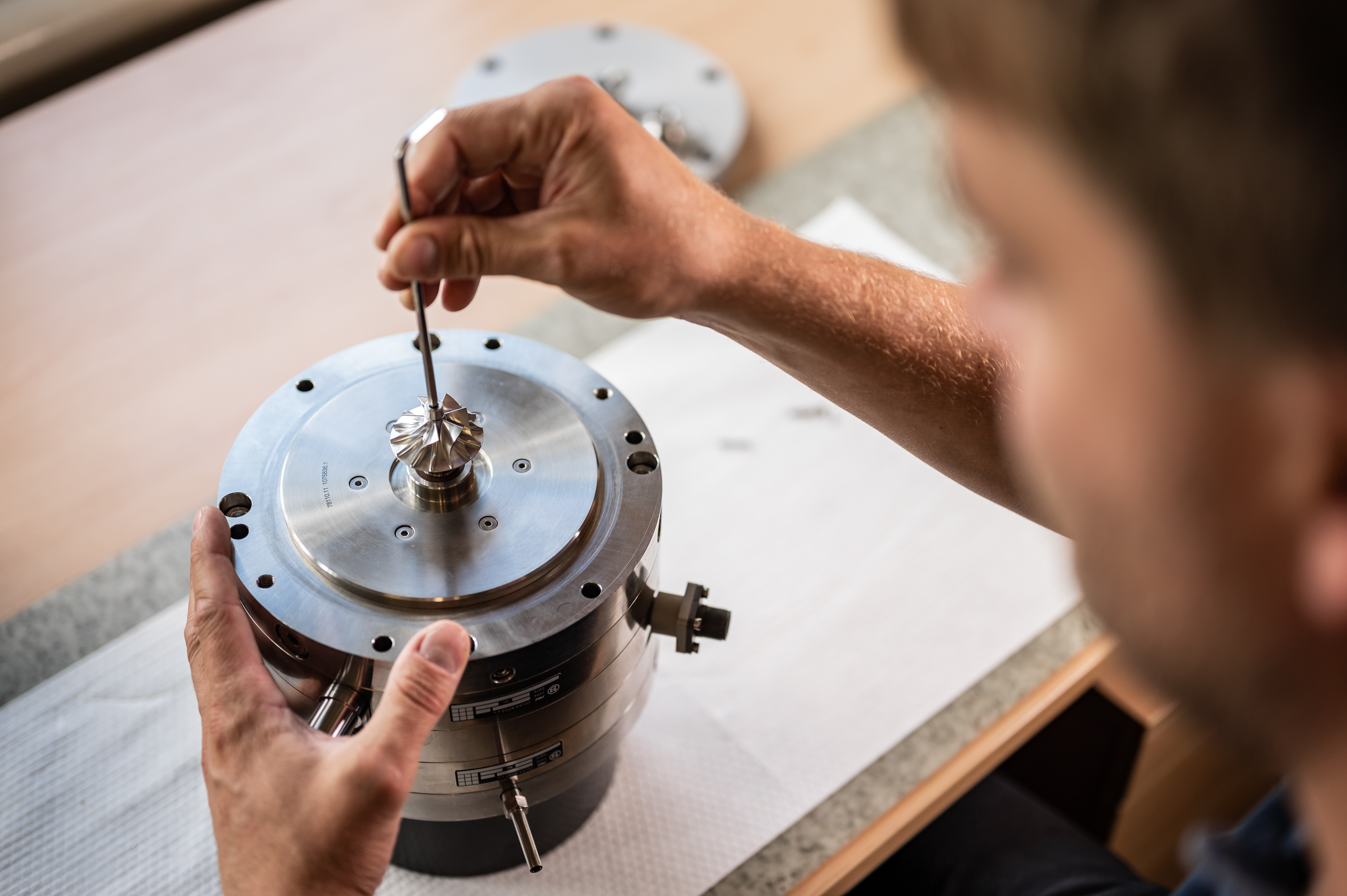  PBS Velka Bites has been in the cryogenic business for more than 35 years. Today, its cryogenics engineering capabilities include everything from preliminary calculation through design, manufacturing and assembly, to testing and user optimization of its cryogenic products. Since the late ’80s, PBS has been developing and supplying cryogenic turbines for the liquefaction of helium. Both liquid and gaseous helium applications must meet extremely demanding technical requirements not only in the design and construction phase but also in terms of production processes, final assembly and testing. PBS became one of the few companies in the world able to independently provide all these stages of cryogenic device production under one roof. The company’s offering of cryogenic devices has gradually expanded to include turbines and compressors, designed to work with other gases utilized in modern cryogenics. To date, all cryogenic products of PBS have been used for inert gas applications, but their design applies to other gases as well. Today, PBS is a major supplier of cryogenic turboexpanders, compressors, pumps and cryogenic drive units for the world's leading manufacturers of cryogenic products.
PBS Velka Bites has been in the cryogenic business for more than 35 years. Today, its cryogenics engineering capabilities include everything from preliminary calculation through design, manufacturing and assembly, to testing and user optimization of its cryogenic products. Since the late ’80s, PBS has been developing and supplying cryogenic turbines for the liquefaction of helium. Both liquid and gaseous helium applications must meet extremely demanding technical requirements not only in the design and construction phase but also in terms of production processes, final assembly and testing. PBS became one of the few companies in the world able to independently provide all these stages of cryogenic device production under one roof. The company’s offering of cryogenic devices has gradually expanded to include turbines and compressors, designed to work with other gases utilized in modern cryogenics. To date, all cryogenic products of PBS have been used for inert gas applications, but their design applies to other gases as well. Today, PBS is a major supplier of cryogenic turboexpanders, compressors, pumps and cryogenic drive units for the world's leading manufacturers of cryogenic products.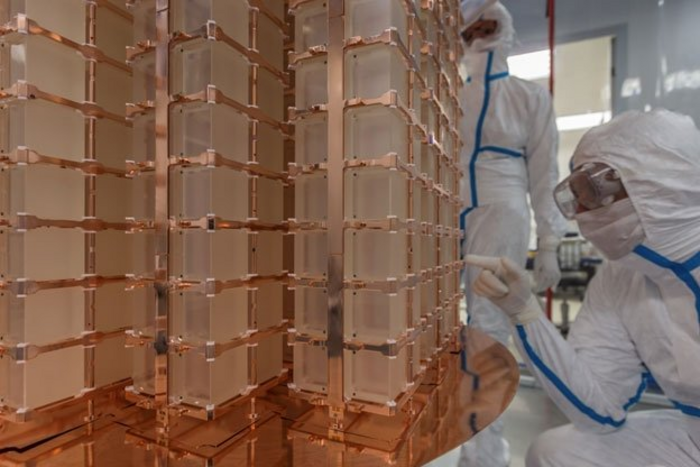  There is so much that we do not yet know about neutrinos.
There is so much that we do not yet know about neutrinos.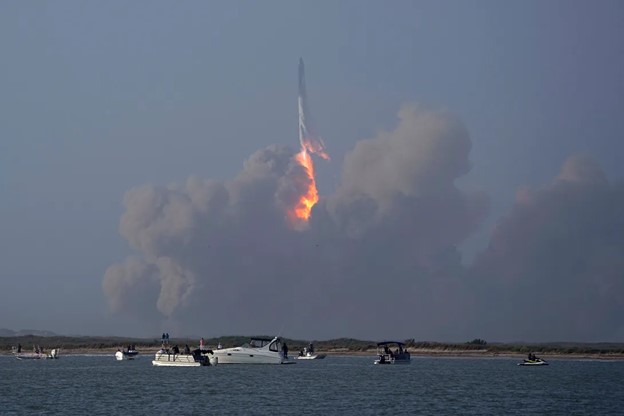  Shortly after
Shortly after With its third company acquisition in just over two years, marine pump specialist, Svanehøj, continues to expand its service solution business, this time by taking over California-based Complete Cryogenic Services (CCS), a specialist in service and overhaul of submerged pumps on LNG tankers.
With its third company acquisition in just over two years, marine pump specialist, Svanehøj, continues to expand its service solution business, this time by taking over California-based Complete Cryogenic Services (CCS), a specialist in service and overhaul of submerged pumps on LNG tankers. 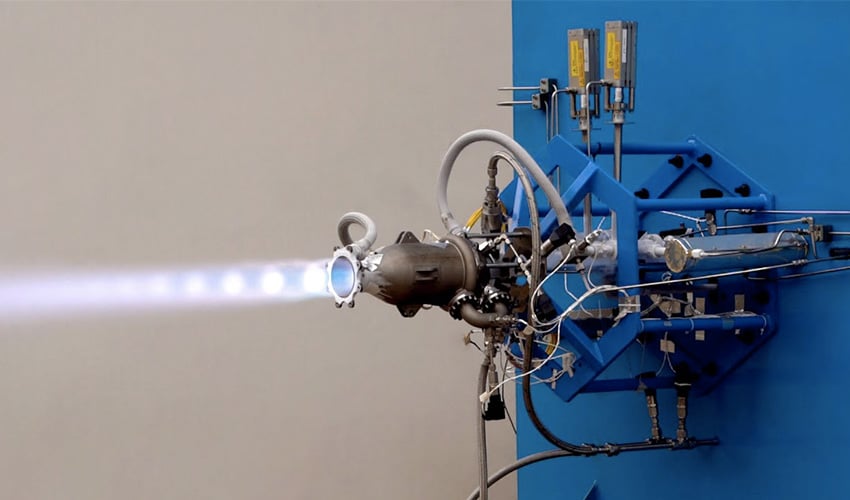 In 2020, the world was introduced to Dhawan-I, a 3D printed cryogenic engine made by Skyroot Aerospace. Three years later, the Indian company has been working on a more powerful model, unveiling to the public the new and improved Dhawan-II, which is said to have successfully completed testing. Like its predecessor, this engine is also 3D printed. Skyroot’s cryogenic rocket engine uses two rocket propellants: liquid natural gas (LNG) and liquid oxygen (LoX), which require temperatures below -150 °C for storage and operation. The tests were conducted at Solar Industries’ propulsion test facility in Nagpur, India.
In 2020, the world was introduced to Dhawan-I, a 3D printed cryogenic engine made by Skyroot Aerospace. Three years later, the Indian company has been working on a more powerful model, unveiling to the public the new and improved Dhawan-II, which is said to have successfully completed testing. Like its predecessor, this engine is also 3D printed. Skyroot’s cryogenic rocket engine uses two rocket propellants: liquid natural gas (LNG) and liquid oxygen (LoX), which require temperatures below -150 °C for storage and operation. The tests were conducted at Solar Industries’ propulsion test facility in Nagpur, India.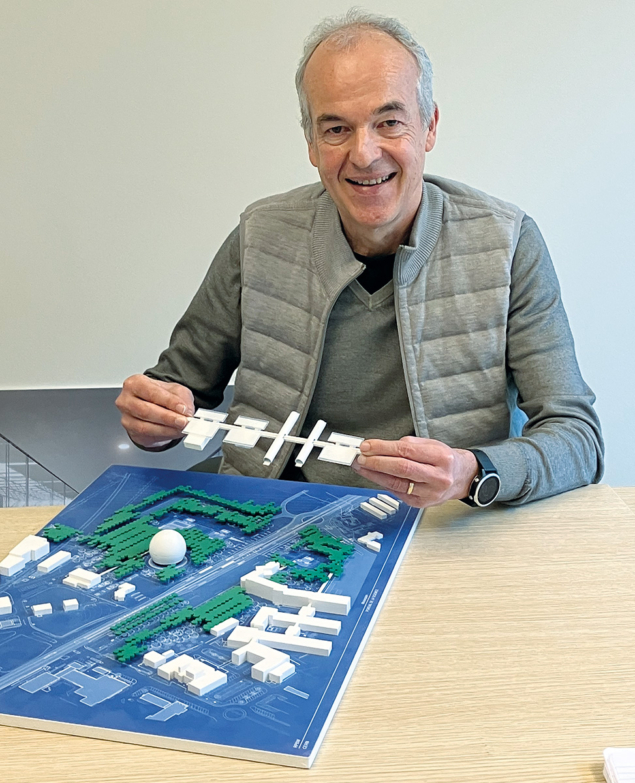 CERN’s new visitor and education center, Science Gateway, due to open this autumn, will welcome up to half a million people each year. Project leader Patrick Geeraert describes how this iconic project came about, how it will operate, and what it aims to achieve.
CERN’s new visitor and education center, Science Gateway, due to open this autumn, will welcome up to half a million people each year. Project leader Patrick Geeraert describes how this iconic project came about, how it will operate, and what it aims to achieve.
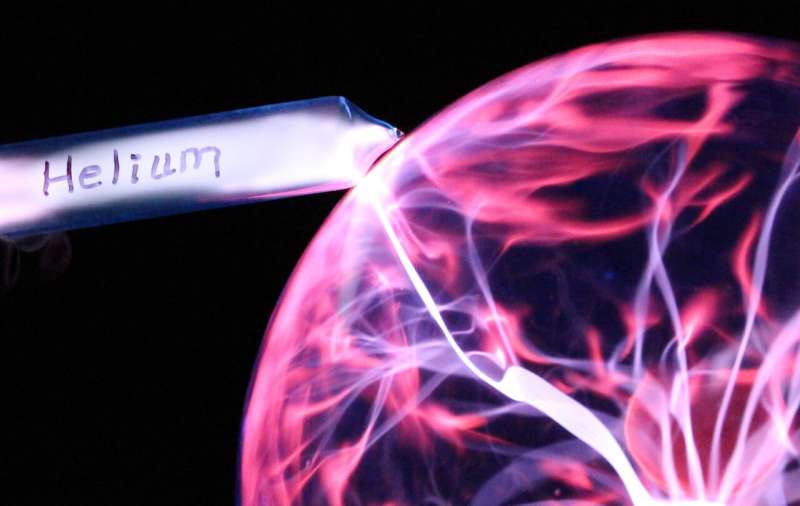 Research led by the University of Oxford could help overturn the current supply crisis of helium, a vital societal resource. The study proposes a new model to account for the existence of previously unexplained helium-rich reservoirs. The findings, published in Nature, could help locate untapped reservoirs of accessible helium. Dr. Anran Cheng (Department of Earth Sciences, University of Oxford), lead author of the study, says, "Our model shows the importance of factoring in the high diffusivity of helium and the long timescales needed to accumulate significant gas quantities, and the fact that the entire geological system acts dynamically to affect the process. This model provides a new perspective to help identify the environments that slow helium gases down enough to accumulate in commercial amounts."
Research led by the University of Oxford could help overturn the current supply crisis of helium, a vital societal resource. The study proposes a new model to account for the existence of previously unexplained helium-rich reservoirs. The findings, published in Nature, could help locate untapped reservoirs of accessible helium. Dr. Anran Cheng (Department of Earth Sciences, University of Oxford), lead author of the study, says, "Our model shows the importance of factoring in the high diffusivity of helium and the long timescales needed to accumulate significant gas quantities, and the fact that the entire geological system acts dynamically to affect the process. This model provides a new perspective to help identify the environments that slow helium gases down enough to accumulate in commercial amounts." German-based H2FLY has announced success from a liquid hydrogen filling test of its HY4 hydrogen-electric aircraft. The on-ground test at Air Liquide’s Campus Technologies Grenoble in France saw liquid hydrogen fill the aircraft’s new liquid hydrogen storage system, designed and supplied by Air Liquide. Coming as a precursor to future tests in which the storage system will be coupled with H2FLY’s fuel cell system to form a complete hydrogen-electric powertrain, the test comes as a milestone in the steps to achieving hydrogen-powered flight for the Stuttgart company.
German-based H2FLY has announced success from a liquid hydrogen filling test of its HY4 hydrogen-electric aircraft. The on-ground test at Air Liquide’s Campus Technologies Grenoble in France saw liquid hydrogen fill the aircraft’s new liquid hydrogen storage system, designed and supplied by Air Liquide. Coming as a precursor to future tests in which the storage system will be coupled with H2FLY’s fuel cell system to form a complete hydrogen-electric powertrain, the test comes as a milestone in the steps to achieving hydrogen-powered flight for the Stuttgart company.
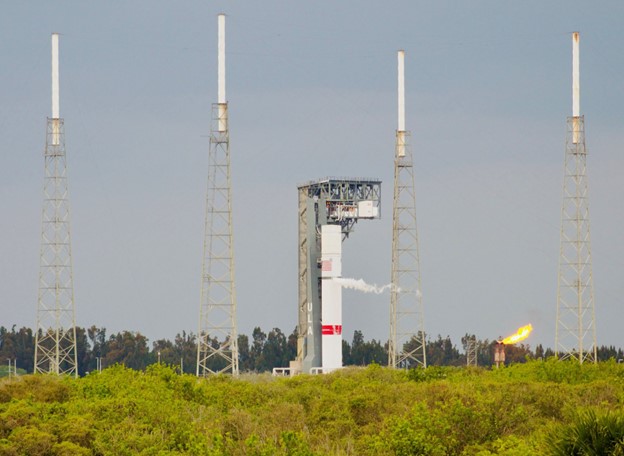 Completing the next phase of testing in preparation for the inaugural Vulcan rocket flight, the United Launch Alliance (ULA) team accomplished tanking demonstrations at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station, Florida. The pathfinder tests filled the Vulcan first stage and Centaur V upper stage with cryogenic propellant on separate days to validate performance of the stages, Vulcan Launch Platform (VLP), Space Launch Complex-41 facilities and ground support systems.
Completing the next phase of testing in preparation for the inaugural Vulcan rocket flight, the United Launch Alliance (ULA) team accomplished tanking demonstrations at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station, Florida. The pathfinder tests filled the Vulcan first stage and Centaur V upper stage with cryogenic propellant on separate days to validate performance of the stages, Vulcan Launch Platform (VLP), Space Launch Complex-41 facilities and ground support systems.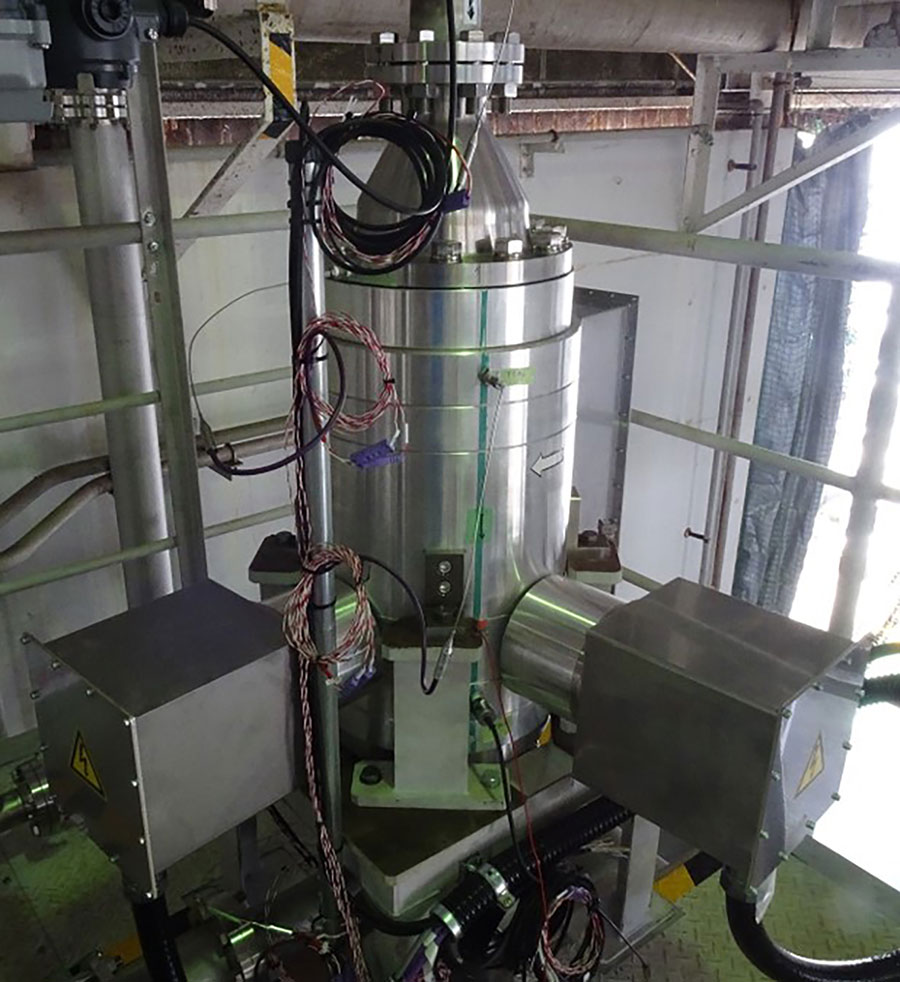 Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. (MHI) and Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Marine Machinery and Equipment Co., Ltd. (MHI-MME), a wholly owned operating company of MHI based in Nagasaki, have successfully conducted demonstration testing of 100 kW class cryogenic ORC (Organic Rankine Cycle) power generation using the world’s first “next-generation oilless cryogenic turbine generator.” The innovative generator adapts the turbine generator featuring a hermetically sealed oilless structure, of the kind used in ORC generation, to cryogenic power generation. The testing demonstrated that with use of liquid nitrogen as the cryogenic energy source it is possible to secure a stable refrigerant cycle and the specified regeneration output without freezing-induced clogging, etc. even under conditions more severe than the low temperatures of conventional LNG (liquefied natural gas) cryogenic generation.
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. (MHI) and Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Marine Machinery and Equipment Co., Ltd. (MHI-MME), a wholly owned operating company of MHI based in Nagasaki, have successfully conducted demonstration testing of 100 kW class cryogenic ORC (Organic Rankine Cycle) power generation using the world’s first “next-generation oilless cryogenic turbine generator.” The innovative generator adapts the turbine generator featuring a hermetically sealed oilless structure, of the kind used in ORC generation, to cryogenic power generation. The testing demonstrated that with use of liquid nitrogen as the cryogenic energy source it is possible to secure a stable refrigerant cycle and the specified regeneration output without freezing-induced clogging, etc. even under conditions more severe than the low temperatures of conventional LNG (liquefied natural gas) cryogenic generation.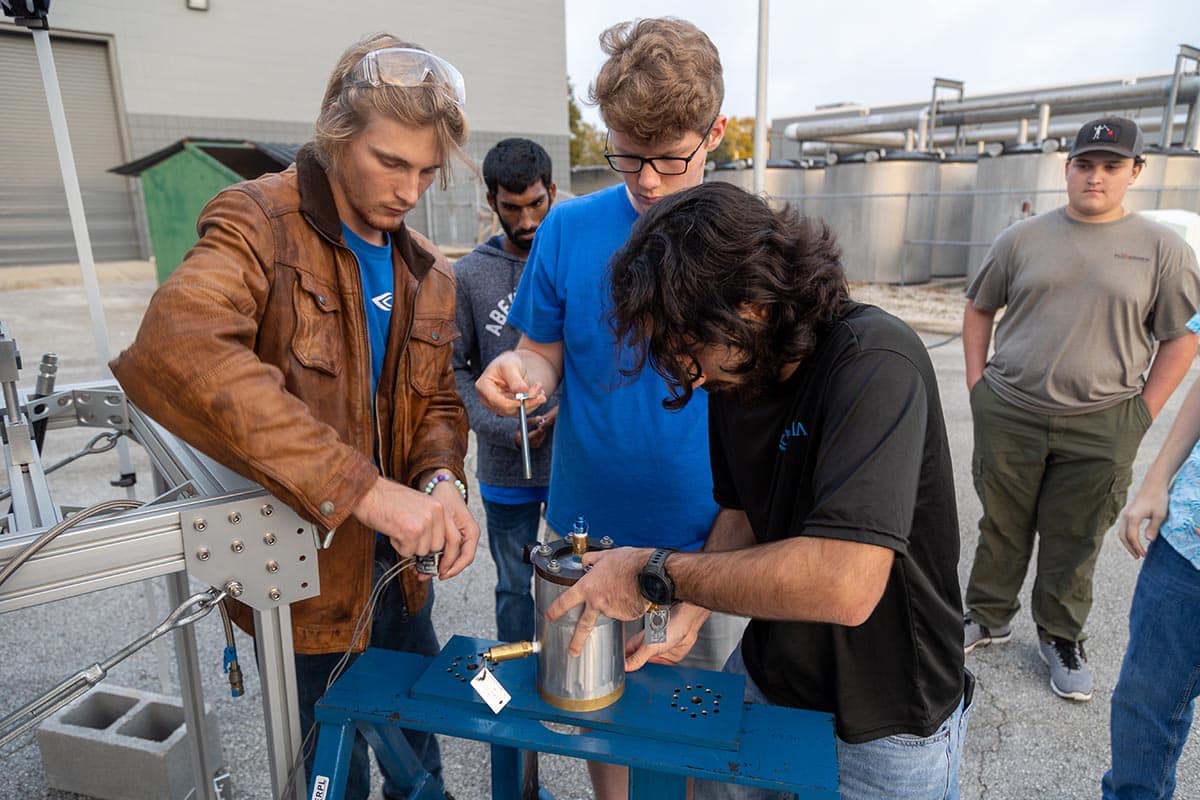 Aerospace Engineering students Alex Clay and Samir Ahmed have spent the past four years at Embry-Riddle Aeronautical University manufacturing complex liquid-propellant rocket engines. Now, as they near graduation, there is one last thing they’d like to do: Prepare for ignition. Along with fellow members of the university’s Experimental Rocket Propulsion Laboratory (ERPL), the two have built a state-of-the-art fuel-feed system in hopes of accomplishing that very goal. If successful, the hardware will offer future generations of rocketry students a safe and consistent way to field test their designs — which, according to sophomore Aerospace Engineering student Taylor Koehn, is currently the “most significant bottleneck” in the process of engine building.
Aerospace Engineering students Alex Clay and Samir Ahmed have spent the past four years at Embry-Riddle Aeronautical University manufacturing complex liquid-propellant rocket engines. Now, as they near graduation, there is one last thing they’d like to do: Prepare for ignition. Along with fellow members of the university’s Experimental Rocket Propulsion Laboratory (ERPL), the two have built a state-of-the-art fuel-feed system in hopes of accomplishing that very goal. If successful, the hardware will offer future generations of rocketry students a safe and consistent way to field test their designs — which, according to sophomore Aerospace Engineering student Taylor Koehn, is currently the “most significant bottleneck” in the process of engine building. BCCK, a leader in engineering, procurement, fabrication and field construction services, has applied patent-pending technology, G2R-Flex®, to provide enhanced propane recovery for a premier midstream group in Ohio’s Marcellus-Utica Basin. Utilizing a skidded BCCK patent-pending design, G2R-Flex® improved current 200 MMSCFD GSP facilities' propane recoveries to greater than 99 percent in ethane rejection and can also be applied to improve performance in ethane recovery.
BCCK, a leader in engineering, procurement, fabrication and field construction services, has applied patent-pending technology, G2R-Flex®, to provide enhanced propane recovery for a premier midstream group in Ohio’s Marcellus-Utica Basin. Utilizing a skidded BCCK patent-pending design, G2R-Flex® improved current 200 MMSCFD GSP facilities' propane recoveries to greater than 99 percent in ethane rejection and can also be applied to improve performance in ethane recovery.